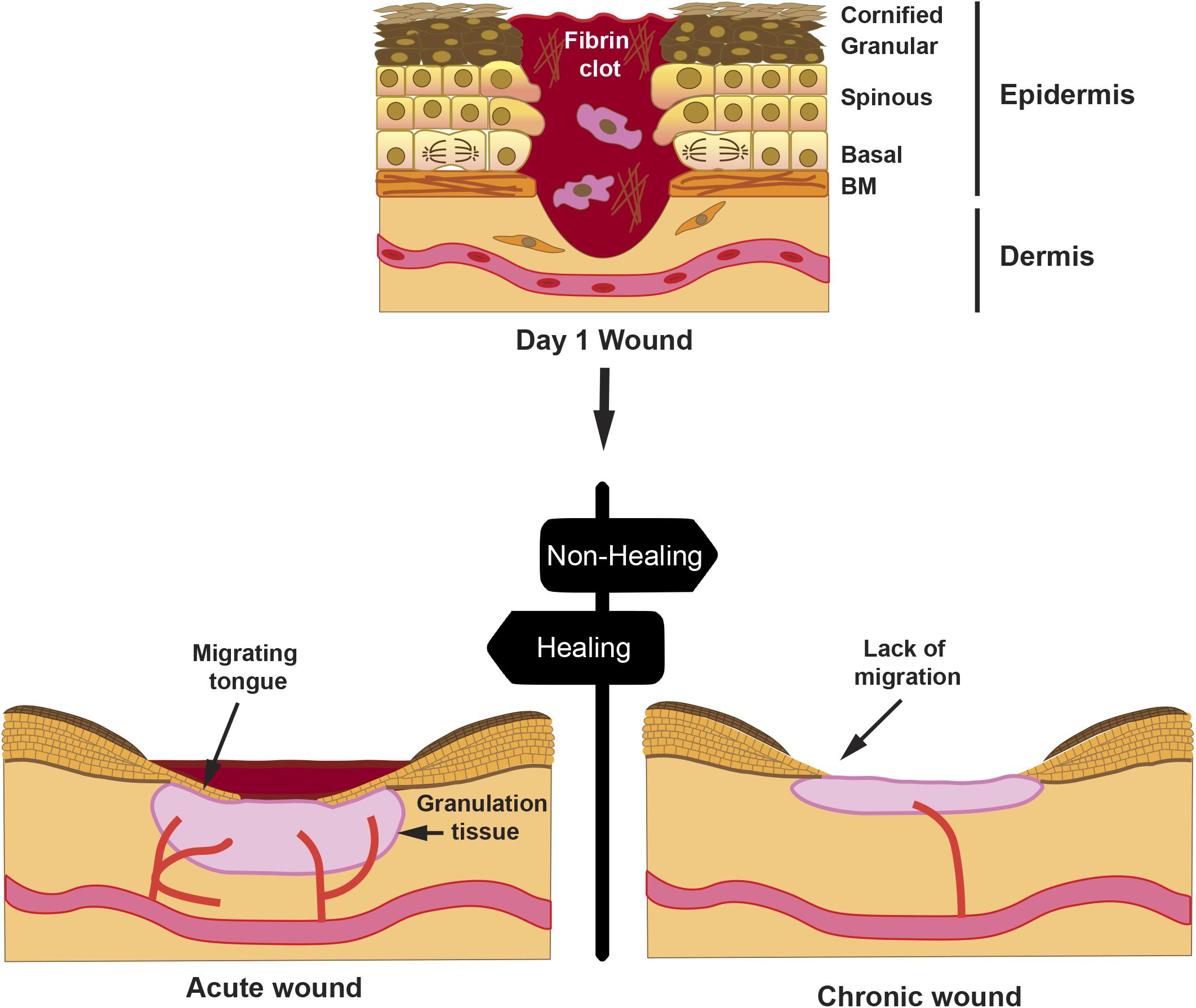
Wound Care
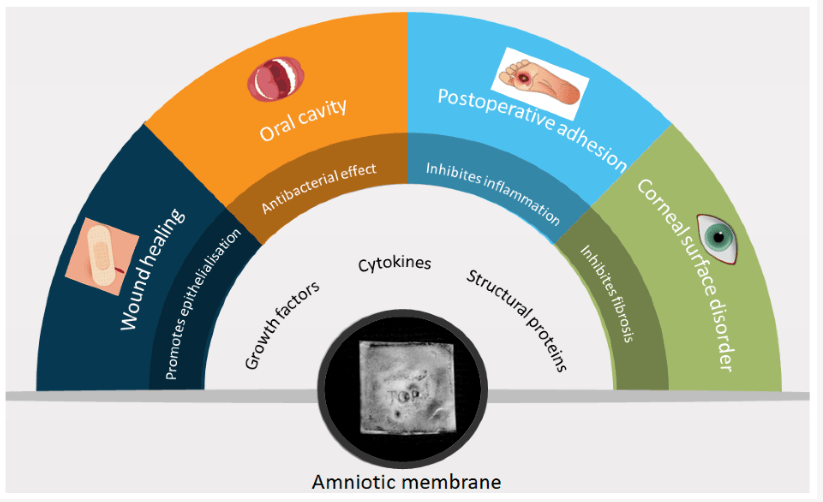
Amniotic Graft
Amniotic membrane grafts have therapeutic potential for wound healing. Early application of amniotic membrane is beneficial in healing ulcers, burns, and dermal injuries. Derived from the innermost layer of the placenta, amniotic membrane has been used in medical applications for over a century, with its use in wound care gaining significant traction in recent years due to its unique properties and effectiveness.
Analgesic Effect
Amniotic membrane covers loose nerve twigs in a wound and reduces the concentration of anti-inflammatory and algic cytokines and peptides which significantly reduces pain in the wound spot. This pain-reducing effect is particularly beneficial for patients with chronic wounds or burns, improving their quality of life during the healing process.
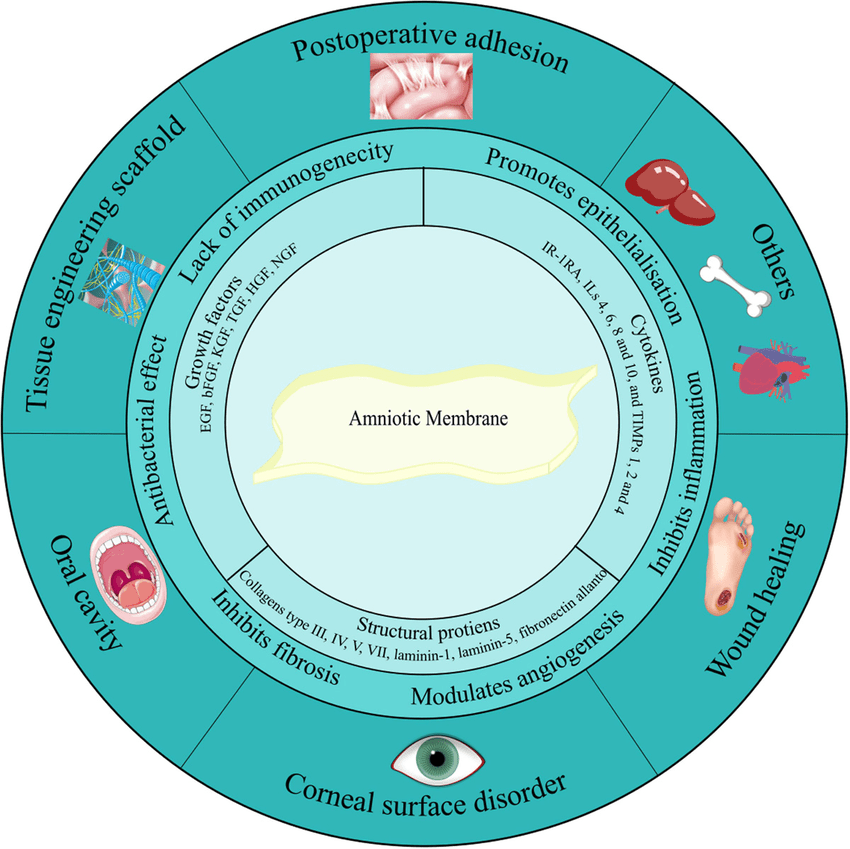
Reducing Scarring
One of the amniotic membrane’s surfaces is non-adhesive, prevents from growing, and reduces occurring of undesired accretions and fibrotization. The hyaluronic acid present in the amniotic membrane also inhibits excessive fibrotization. This anti-scarring property is especially valuable in cosmetically sensitive areas or in cases where scar tissue might impair function.
Epithelization
Amniotic membrane contains tens of types of growth factors many of which directly and significantly supports epithelization. It especially contains epidermal growth factor (EGF), keratinocyte growth factor (KGF), and hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) which support and activate migration, proliferation, and differentiation of epithelial cells. This promotes faster wound closure and re-epithelialization, which is crucial for protecting the wound from infection and further damage.
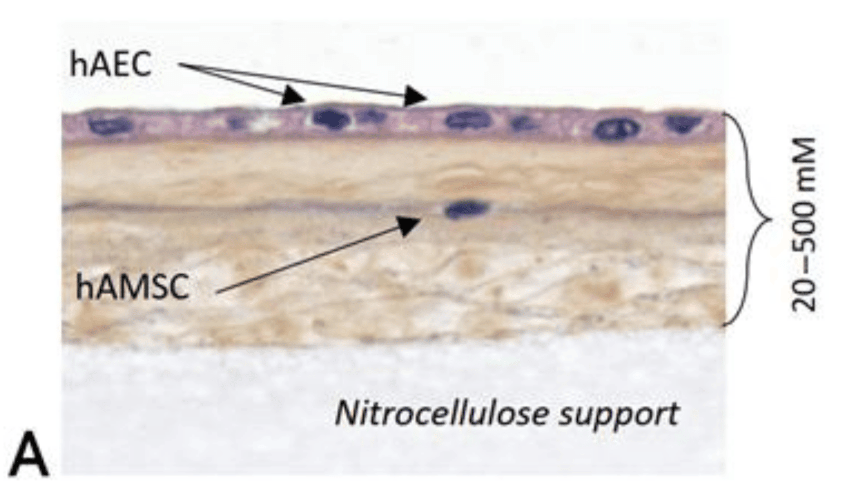
Angiogenic Effect
Angiogenesis is a very important stage in the repair of skin ulcers, these cells can be very suitable for the accelerating of wound healing process. Amniotic membrane releases a range of angiogenic factors into the wound, especially bFGB (Fibroblast Growth Factor-basic), TGF-ß (Transforming Growth Factor-beta) which support vessel renewal in the area of the healing wound. Neoagiogenesis augmented by the amniotic membrane significantly shortens the time to regenerate. This enhanced blood supply brings more oxygen and nutrients to the wound site, accelerating the healing process.
Anti-inflamMatory Effect
Amniotic membrane contains and releases Interleukin 10 (IL-10) which has the major anti-inflammatory effect, and thrombospondin-1, both are antagonists of the Interleukin 1 (IL-1) receptor and tissue inhibitors metalloproteinases (TIMPs). Infection and inflammation are two serious drawbacks in the wound care process. Therefore, skin substitutes should exhibit an appropriate anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties. AECs express secretory leukocyte proteinase inhibitor (SLPI) and elafin which have anti-inflammatory properties. In addition, they both are a part of amnion’s innate immune system which prevents infection. This anti-inflammatory effect is particularly beneficial in chronic wounds where persistent inflammation can delay healing.
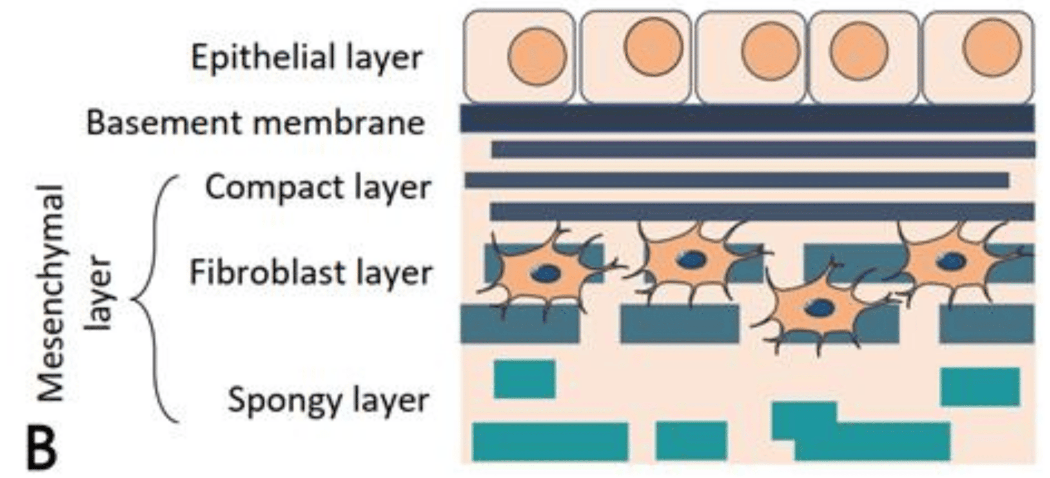

MECHANICAL Effect
Amniotic membrane significantly reduces wound desiccation, and functions as a mechanical support and structure which allows epithelial and mesenchymal cells attachment, motility, and proliferation. Amniotic membrane is an appropriate matrix for tissue engineering. It serves as a natural scaffold, providing a supportive environment for cell growth and tissue regeneration. This mechanical protection is especially important in exposed wounds or those in high-movement areas.
Drug-reservoir CAPACITY
Amniotic membrane has a drug reservoir capacity. Human amniotic cells also have the ability to store drugs and release them continuously in the body. Amniotic cells used as a sustained release drug delivery system for wound healing. Thickness of the AM has a direct effect on its drug release kinetic. This unique property allows for the incorporation of additional therapeutic agents into the graft, providing a sustained release mechanism that can further enhance wound healing or combat infection.

APPLICATION IN WOUND CARE
Amniotic membrane grafts have shown promising results in treating a variety of wounds, including:
- Diabetic foot ulcers
- Venous leg ulcers
- Pressure ulcers
- Burn wounds
- Surgical wounds
- Ophthalmological applications (corneal reconstruction)
The versatility of amniotic membrane grafts makes them a valuable tool in the arsenal of advanced wound care treatments.
